Kvantové previazanie - kvantové šifrovanie - stroj času
Úvod
Tento článok bude venovaný kvantovému previazaniu. Tento článok je úvodom do tejto problematiky, ktorá bola už rozpísaná na blogu robopol.blogspot.com. Závery a detaily budú podrobnejšie opísané v knihe EDQ teória priestoru a času. Kvantové previazanie je fenomenálna vlastnosť mikrosveta kvantovej fyziky. V dnešnej dobe na základe toho staviame prvé kvantové počítače, ktoré v určitých ohľadoch klasické PC predbehnú svetelnou rýchlosťou. Kvantové previazanie je dnes dobre potvrdené a používa sa aj na teleportáciu častíc. Nedávno urobili kvantové previazanie a teleportáciu až na obežnú dráhu Zeme. Tento článok bude špecifický v zmysle výskumu tejto problematiky (úvodný článok).
Kvantové previazanie /Quantum entanglement
Pokiaľ čitateľ nevie, čo je kvantové previazanie je potrebné si tento pojem vyhľadať, pozrieť.
Bez základných znalosti nebude tento článok celkom zrozumiteľný.
Kvantové previazanie je fyzikálny jav, ktorý nastáva, keď skupina častíc vznikne alebo spolu interaguje spôsobom, ktorý vylučuje, aby ich kvantové stavy boli popísané nezávisle. Potom existuje iba kvantový stav celého systému.
zdroj: wikipedia
Schematický je v EDQ teórii znázornený kvantový pár takto:
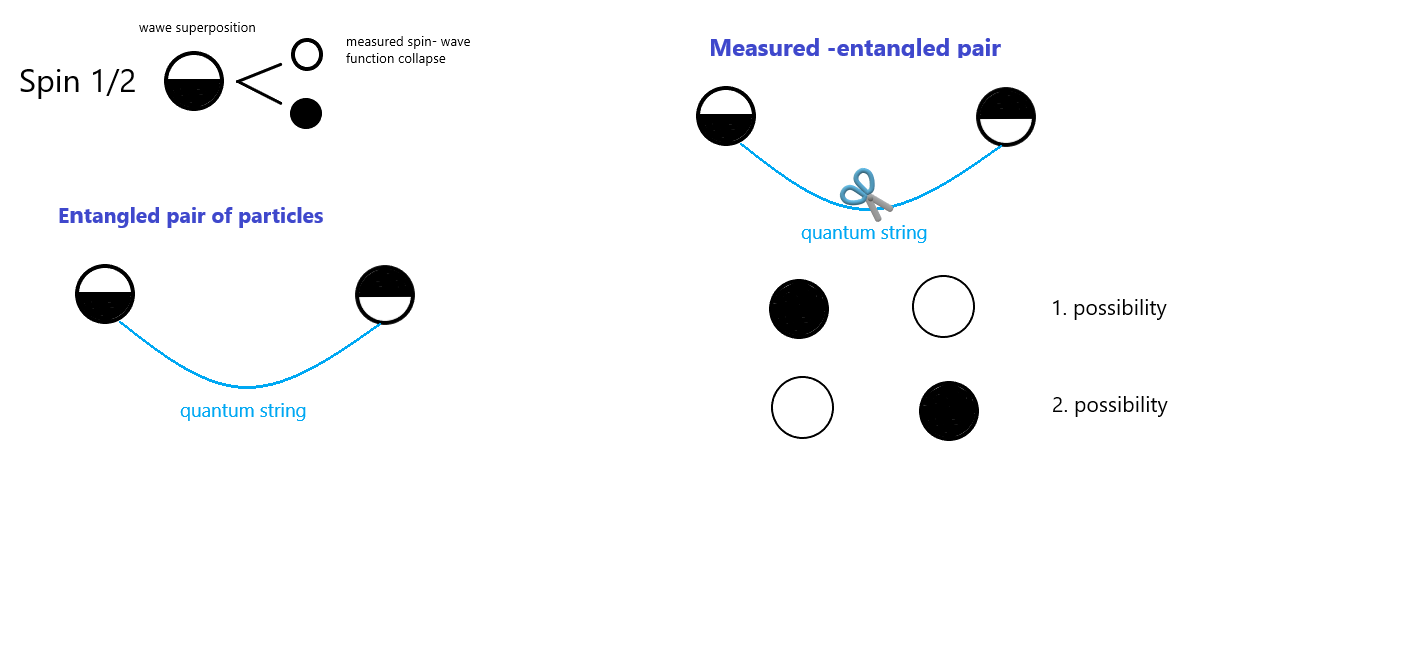
Obr. 1. Schematické, kvantové previazanie v EDQ teórii, zdroj: vlastný obrázok.
Na obrázku je schematický označený previazaný pár častíc so spinom ½. To znamená, že samotná častica môže nadobudnúť iba dva stavy (čierny, biely). To, čo pod samotným spinom rozumieme nie je nateraz dôležité (ide o vnútorný moment hybnosti častice). Einstein sa pokúšal prísť na túto záhadu (EPR paradox), no neuspel. Nazval toto pôsobenie ako strašidelné pôsobenie na diaľku, ktoré sa šíri rýchlejšie ako svetlo ( v podstate nekonečnou rýchlosťou, okamžité spojenie).
Myšlienkový experiment na prenos informácii pomocou previazaných párov - od autora robopol
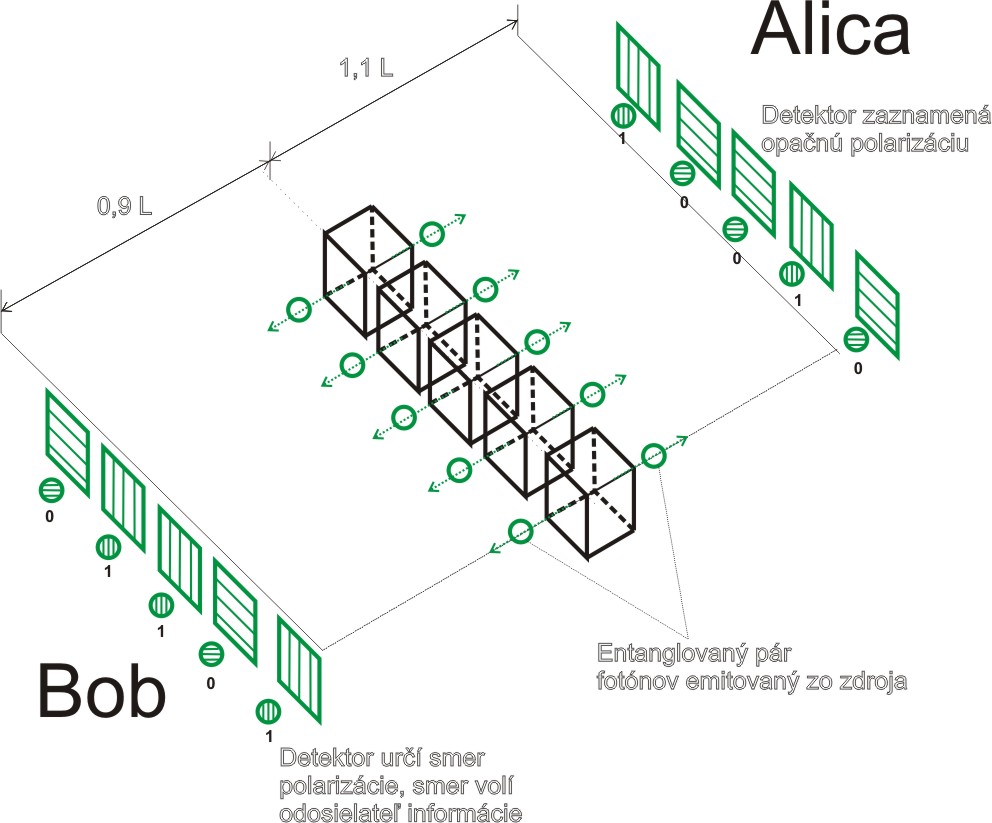
Obr. 2 Pokus s kvantovým previazaním na prenos informácii, kvantové šifrovanie, zdroj: vlastný obrázok.
Popis pokusu
Na obr. č.2 je zhruba v strede zdroj entanglovaných fotónov, ktorý vysiela dvojicu fotónov (jeden k Alici, druhý k Bobovi). Bob je bližšie k zdroju fotónov 0,9L, Alica je 1,1L. Bob chce poslať zmysluplnú šifrovanú informáciu k Alici, ktorú by mohla rozlúštiť iba Alica. Má na to sadu polarizátorov, v rade za sebou. Alica ma taktiež obdobnú sadu. Technické detaily nie je nutné popisovať, pretože ide o myšlienkový pokus a nič z toho, čo by sa nedalo technicky realizovať súčasnou technológiou.
Dohodnú sa predtým na pravidlách:
- Polarizátor môže byt nastavený vertikálne, alebo horizontálne, aby zvislo a rovnobežne bolo to iste na oboch stranách u Alice a Boba, kalibrujú si najskôr smery merania.
- Zvislý polarizovaný fotón bude znamenať "1", vodorovne bude znamenať "0". V tomto myšlienkovom experimente budú odosielať binárny kód, od Boba k Alici.
- Pretože je Bob bližšie on urobí meranie ako prvý, čim donúti fotóny ku konkrétnej polarizácii, alebo zvislo, alebo vodorovne, nedokáže ale vnútiť polarizáciu, takže štatisticky dostane ½ z celého súboru fotónov do požadovanej polarizácie.
- Požadovanú polarizáciu si určuje Bob nastavením zvislo alebo vodorovne.
- Alica si na svojej strane nastavuje smery taktiež, podľa svojho uváženia – teda náhodne. Nemá žiadnu informáciu o tom, ako bude prilietavajúci fotón polarizovaný. Na obrázku je celá sada polarizátorov, každý jeden polarizátor bude symbolizovať podľa nastavenia "1" alebo "0".
Bob nastaví každý jeden polarizátor v rade tak, aby vytvoril želaný binárny kód. Alica na druhej strane bude chcieť rozlúštiť tento kód.
Pokiaľ by sa podarilo čistou náhodou u Boba nastaviť polarizátor v rade tak, že prilietavajúci fotón by si zvolil smer polarizácie zhodný s Bobovým želaním, potom prilietavajúce fotóny k Alici už MAJÚ URČENÚ POLARIZÁCIU (INVERZNÚ k Bobovi). To Alica vie, že jej správne nastavenia musia byť inverzné k polarizácii u Boba. Keby čírou náhodou mala aj ona nastavené správne svoje zariadenia v rade, potom by mala informáciu od Boba cca 2 krát rýchlejšie ako klasickou cestou.
Z hľadiska štatistiky to, ale takto ideálne nebude. Preto je nutné zaviesť toto pravidlo:
- Pokiaľ Bob nedosiahne požadovanú polarizáciu a to sa dozvie tak, že fotón neprejde polarizátorom, Bob posiala informáciu k Alici klasickou cestou, napr. cez vysielačku, označí "FALSE". Urobí to na každom jednom polarizátore v rade za sebou, kde nedošlo k želanej polarizácii Boba.
- Zo štatistického hľadiska by to malo byť okolo ½ polarizátorov správne.
Rekonštrukcia informácie u Alici:
Alica ma nejak nastavené svoje zariadenie postupne. Na každom zariadení zistí, či fotón prešiel alebo neprešiel. Ak prešiel a nemá od boba informáciu "FALSE", potom je nastavenie správne. Pokiaľ jej fotón prešiel, ale ma k tomu správu od Boba FALSE, tak urobí inverziu polarizácie. Tretia možnosť je ta, že jej neprejde žiaden fotón a nemá od Boba FALSE, potom urobí inverziu k nastaveniu polarizatora. Posledná možnosť je neprešiel fotón a má informáciu od Boba FALSE, potom mala správne natočený polarizátor k Bobovi. Takto zrekonštruuje celu informáciu. Je to šifrovaná informácia, nie je ju možne nijak prelomiť, zrekonštruovať to dokáže iba Alica.
Záver kvantového šifrovania
Okrem toho, že sme poslali šifrovanú informáciu poslali sme štatisticky iba polovicu oprav. Je však, ale jasne aj to, že pokiaľ by sa neposielalo nič (nulové opravy) šťastnou náhodou, tak prostredníctvom previazania to vieme urobiť nad svetelnou rýchlosťou. Je zrejme, že niečo bolo len zaslané nad svetelnou rýchlosťou. Nad svetelnou rýchlosťou bol zaslaný šifrovaný podklad a zasielané opravy sú kľúč k dešifrovaniu (zaslané klasickou cestou rýchlosťou svetla). Zaujímavé bude sledovať tento experiment z nejakej letiacej sústavy voči sústave BOB-ALICA, objaví sa zaujímavý fenomén. Nelokálnosť dokáže urobiť značné problémy s pojmom relativita súčasnosti.
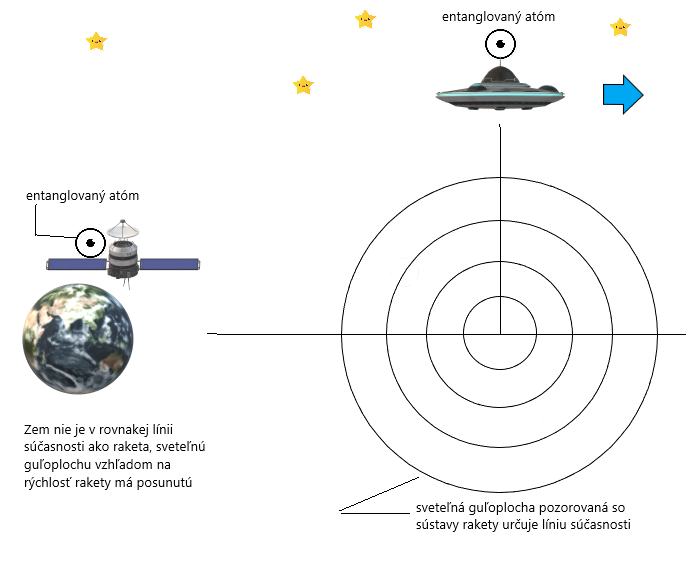
Ako poslať informáciu rýchlejšie ako svetlo aj naprieč času?
Mame Alicu na planéte Zem, Bob odlieta vyspelou kozmickou raketou na cestu do vesmíru. Alica a Bob majú zariadenie, kde majú entanglované častice, dnes je možné previazať aj atómy, aj sadu atómov. Pred odletom Boba si previažu svoje častice. Dohodnú sa na rovnakých pravidlách ako predtým. Budú merať na svojich previazaných časticiach - spiny. Máme častice s ½ spinom, ktoré môžu nadobudnúť smer hore alebo dole. Ostatné pravidla ostávajú, až na jedno. NEZÁLEŽÍ NA TOM KTO PREVEDIE MERANIE AKO PRVÝ, je ale veľmi dôležité, aby to bolo s minimálnou časovou odchýlkou(oneskorením). Dôležité pravidlo je to, že ak je nameraný spin hore symbolizuje to "1", ak je nameraný spin dole symbolizuje to "0". Teda binárny kód.

Obr.3 Abstraktný obrázok, zdroj : internet.
Dohodnú si aj presný plán letu s Bobom, majú presné atómové hodiny, aj Alica aj Bob. Bob pôjde presne v stanovených rýchlostiach, v presných dohodnutých časoch, po fáze zrýchlenia Bobovej rakety v presne zadefinovanom čase pôjde ďalej zotrvačnosťou.
V určitej vzdialenosti od planéty začnú prevádzať v presne dohodnutých časoch merania spinov na svojich časticiach. Máme obdobnú sadu častíc, aby bolo možné poslať zmysluplnú informáciu. Pre binárny kód ich potrebujeme veľa. No, aby prebehlo meranie skoro súčasne je potrebné zohľadniť všeobecnú relativitu, kde hodiny netikajú rovnako z dôvodu gravitačného poľa a vzájomnej rýchlosti. Je dokonca posunutá súčasnosť. Chce to zložitejšie výpočty a odpočty od týchto efektov.
Takže Alica prevedie všetky merania na svojich časticiach. Ak by to Alica urobila ako prvá, potom Bob ma už určené spiny, ktoré nameria na svojich časticiach. Platí to aj obrátene. Ak posiela Bob informáciu Alici posiela chybové hlásenia on "false", presne v zmysle predošlého článku (vyšle signál rýchlosťou svetla k Alici s opravami). Ak vysiela informácie Alica, posiela ona chybové hlásenia Bobovi. Rýchlosť svetla signálu doženie raketu. Rozkódujú svoje informácie rovnako, ako v predchádzajúcom popise.
Pri šťastnej náhode namerané spiny budú v zhode pre Boba s jeho požadovanou informáciou, ktorú chce zaslať Alici. Alici teda neposiela žiadne opravy rýchlosťou svetla! INFORMÁCIA JE ROZKÓDOVATELNÁ PRE ALICU OKAMŽITE V ZMYSLE PRAVIDIEL. DOŠLO K NAD SVETELNÉMU PRENOSU. Vysvetlenie je to, že kvantová informácia je v zhode s Bobovou informáciou. Alica urobí inverziu kvantovej informácie a ma tu Bobovu. To, čo nie je možné sa stalo možné vďaka náhode a kvantovej previazanosti.
Naprieč času
Obr.4 Schematický obrázok pokus s entanglovaným párom v letiacej rakete, zdroj: vlastný obrázok.
Záver
S kvantovou previazanosťou a charakterom vlnovej funkcie v kvantovej mechanike dokážeme poslať informácie aj v čase. Ak by to chcel niekto využiť, tak ho sklamem, keďže Bob sa nachádza na inom mieste ako Alica. Tieto pokusy nenarušili koncept teórie relativity. Lebo jedine, čo sme mohli urobiť je alebo to urobiť v Bobovej súčasnosti, alebo Alicinej, ibaže sme tým okamžite preniesli informáciu do iného času. Ak sa podari raz vnútiť časticiam kvantový stav, čo je dnes vylúčené, potom mame 100% nad svetelný prenos . Je celkom možné (troška šialené), že máme spriahnuté svoje atómy so svojou verziou v budúcnosti, či minulosti, kvantová informácia, totiž narušuje kauzalitu. A zmena stavu v budúcnosti našich atómov (kolaps vlnovej funkcie) môže ovplyvniť naše atómy v súčasnosti.
Pokračovanie príbehu o kvantovej previazanosti bude obsahovať kniha EDQ teória o priestore a čase. Aj nové nápady, čo s tou 50% náhodou. Všimnime si možnú súvislosť s článkom o vzniku vesmíru, konkrétne kvantovou, červou dierou.